GPT-4 is the most advanced Generative AI developed by OpenAI. It is changing the landscape of how we do work. However, GPT-4 is not open-source, meaning we don’t have access to the code, model architecture, data, or model weights to reproduce the results. We cannot create our own GPT-4 like a chatbot.
To balance the scale, open-source communities have started working on GPT-4 alternatives that offer almost similar performance and functionality and require fewer computational resources.
You can learn about GPT-1, GPT-2, GPT-3, and GPT-4 by reviewing: What is GPT-4 and Why Does it Matter?, and master prompt engineering to get better at building end to end data science projects.
In the article, we will introduce 12 GPT-4 alternatives with a brief description and links to the relevant research paper, blog post, chatbot demo, code source, and model card.
Note: Some of the models mentioned have a non-commercial license, which restricts their use to research and academic purposes only. You need to understand these limitations before using them.
1. ColossalChat
ColossalChat is an open-source project that allows you to clone AI models using a complete RLHF (Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback) pipeline.
It is a completely open-source project comprising the bilingual dataset, training code, demo, and 4-bit quantized inference. All the components will help you create a customized chatbot cheaper and faster.
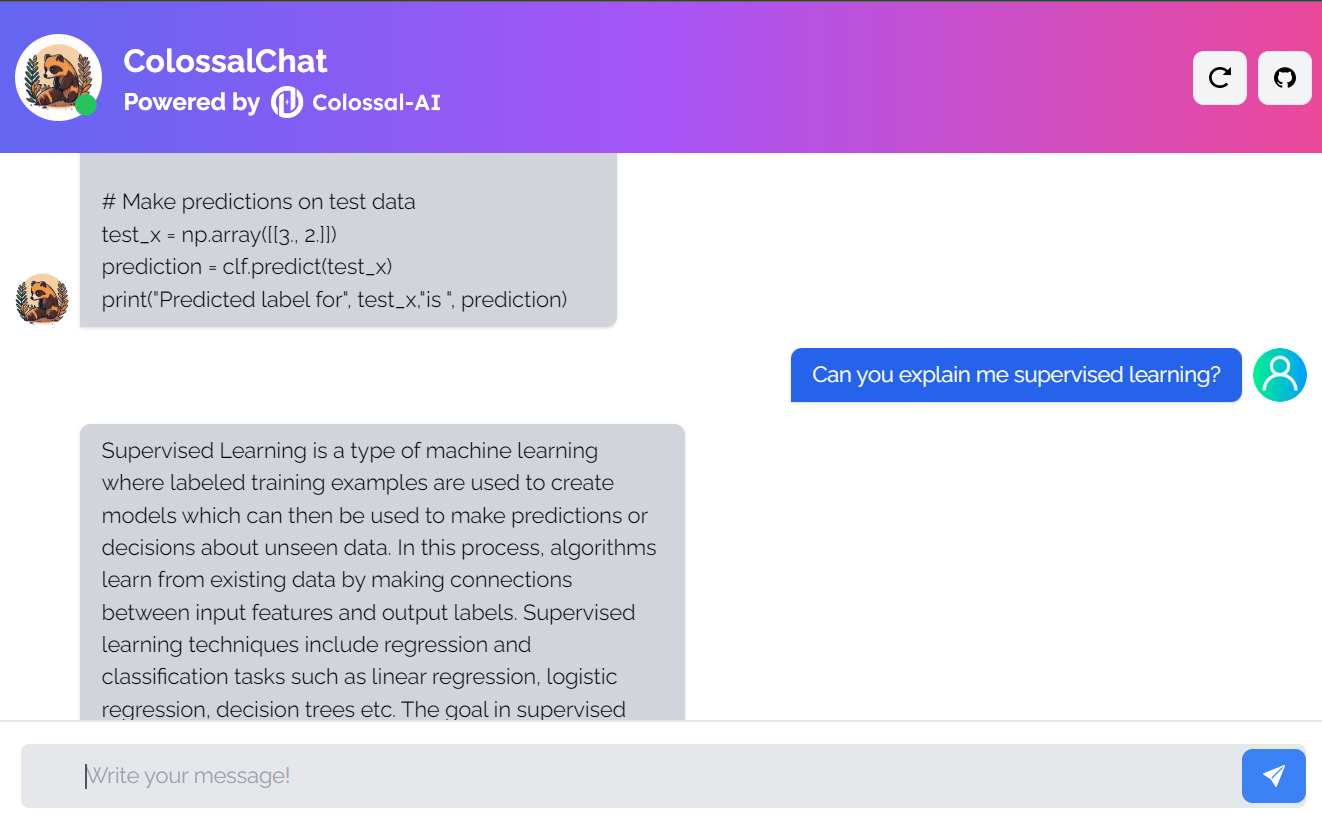
Image from ColossalChat
- Research paper: Colossal-AI: A Unified Deep Learning System For Large-Scale Parallel Training
- Blog post: ColossalChat: An Open-Source Solution for Cloning ChatGPT With a Complete RLHF Pipeline
- GitHub: hpcaitech/ColossalAI
- Demo: ColossalChat (colossalai.org)
2. Alpaca-LoRA
Alpaca-LoRA is a model that was created using the Stanford Alpaca and low-rank adaptation (LoRA). The low-rank adoption allows us to run an Instruct model of similar quality to GPT-3.5 on 4GB RAM Raspberry Pi 4.
The project provides source code, fine-tuning examples, inference code, model weights, dataset, and demo. The best part is that we can train our model within a few hours on a single RTX 4090.
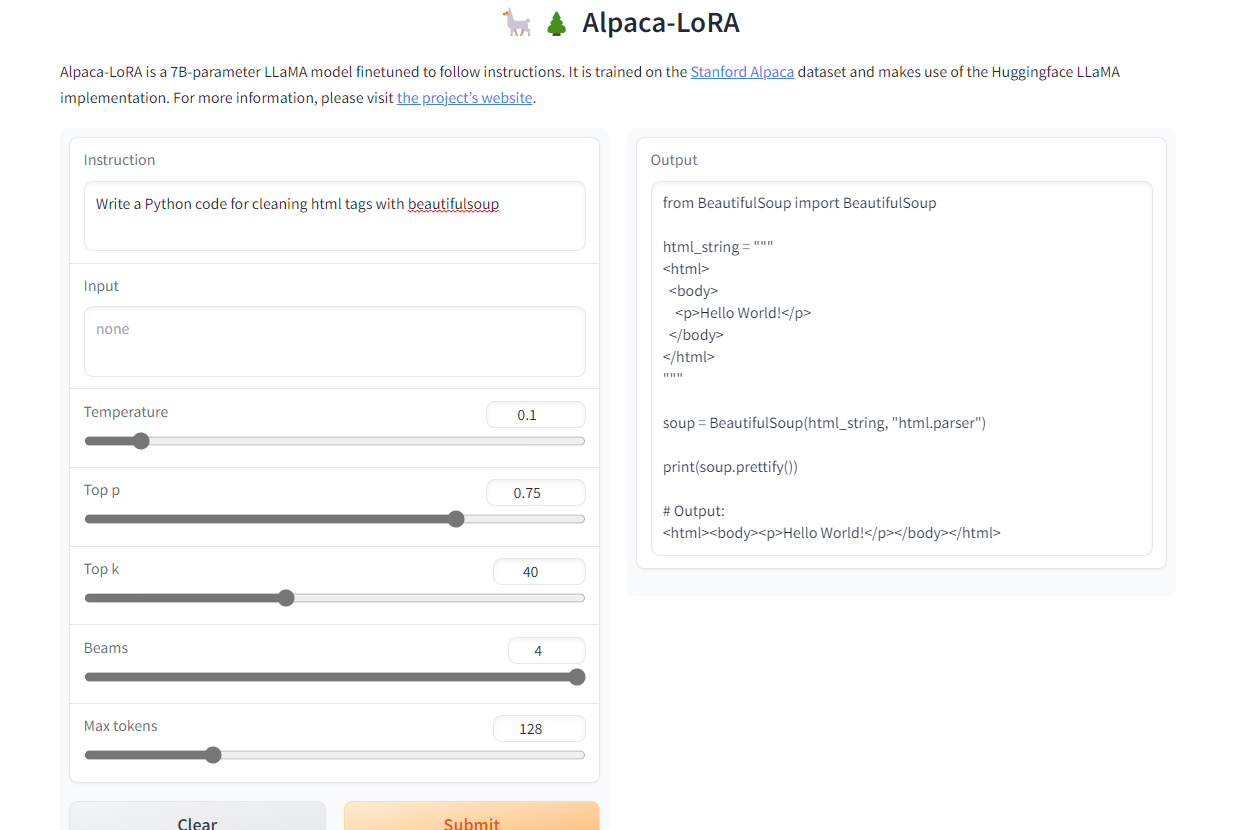
Image from Alpaca-LoRA
- GitHub: tloen/alpaca-lora
- Model Card: tloen/alpaca-lora-7b
- Demo: Alpaca-LoRA
3. Vicuna
The Vicuna can generate coherent and creative text for chatbots. It is a transformer-based architecture that was fine-turned on a conversational dataset collected from ShareGPT.com.
Vicuna provides almost 90% of ChatGPT performance. It is a part of FastChat, an open platform that allows users to train, serve, and evaluate their chatbots. FastChat provides all the necessary components and tools for building a custom chatbot model.
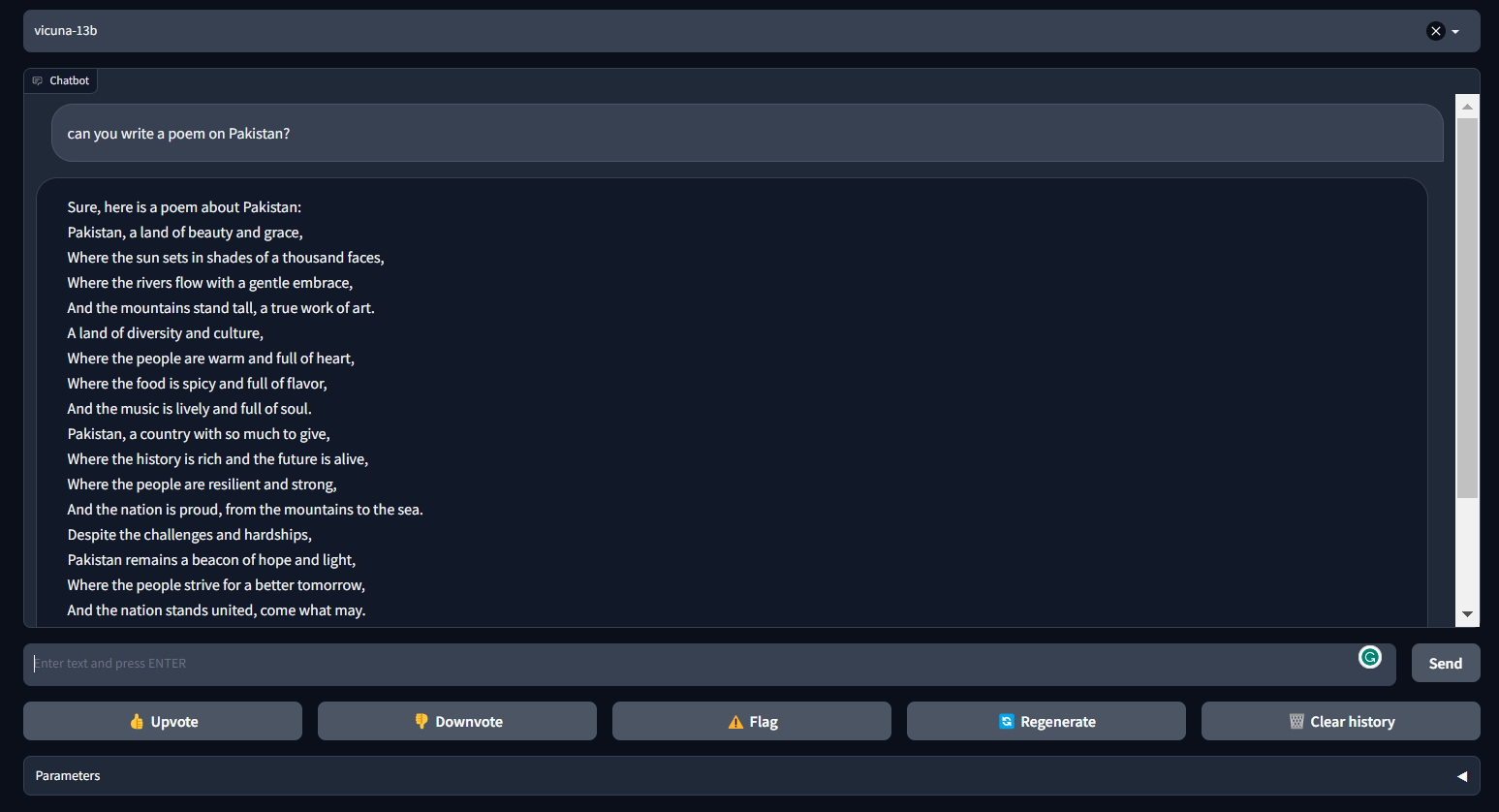
Image from FastChat (lmsys.org)
- Blog post: Vicuna: An Open-Source Chatbot Impressing GPT-4 with 90%* ChatGPT Quality | by the Team with members from UC Berkeley, CMU, Stanford, and UC San Diego
- GitHub: lm-sys/FastChat
- Demo: FastChat (lmsys.org)
4. GPT4ALL
GPT4ALL is a chatbot developed by the Nomic AI Team on massive curated data of assisted interaction like word problems, code, stories, depictions, and multi-turn dialogue. The model architecture is based on LLaMa, and it uses low-latency machine-learning accelerators for faster inference on the CPU.
With GPT4ALL, you get a Python client, GPU and CPU interference, Typescript bindings, a chat interface, and a Langchain backend.
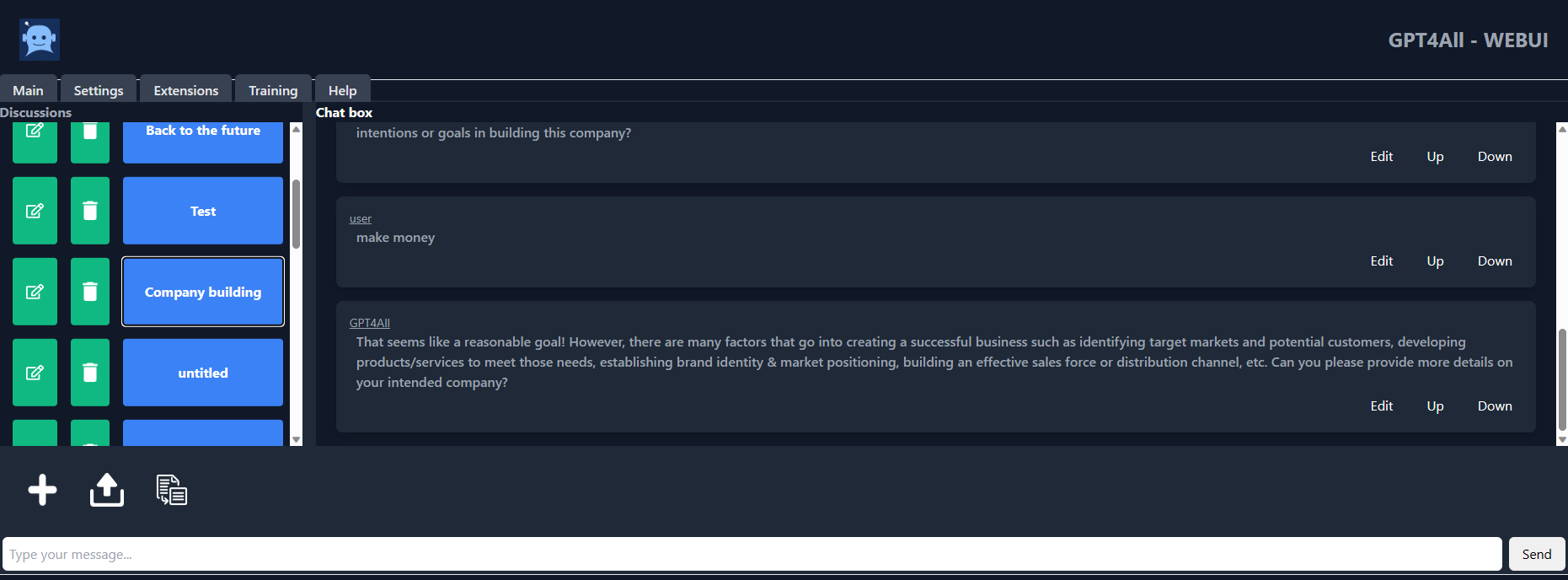
Image from gpt4all-ui
- Technical Report: GPT4All
- GitHub: nomic-ai/gpt4al
- Chatbot UI: nomic-ai/gpt4all-ui
- Model card: nomic-ai/gpt4all-lora
5. Raven RWKV
Raven RWKV is part of ChatRWKV, which is an open-source model like ChatGPT but powered by RWKV (100% RNN) language model, not transformer based.
By utilizing RNNs, the model achieves comparable levels of quality and scalability as transformers, with the added benefits of faster processing speed and VRAM conservation. Raven was fine-tuned to follow instructions, and it was fine-tuned on Stanford Alpaca, code-alpaca, and more datasets.
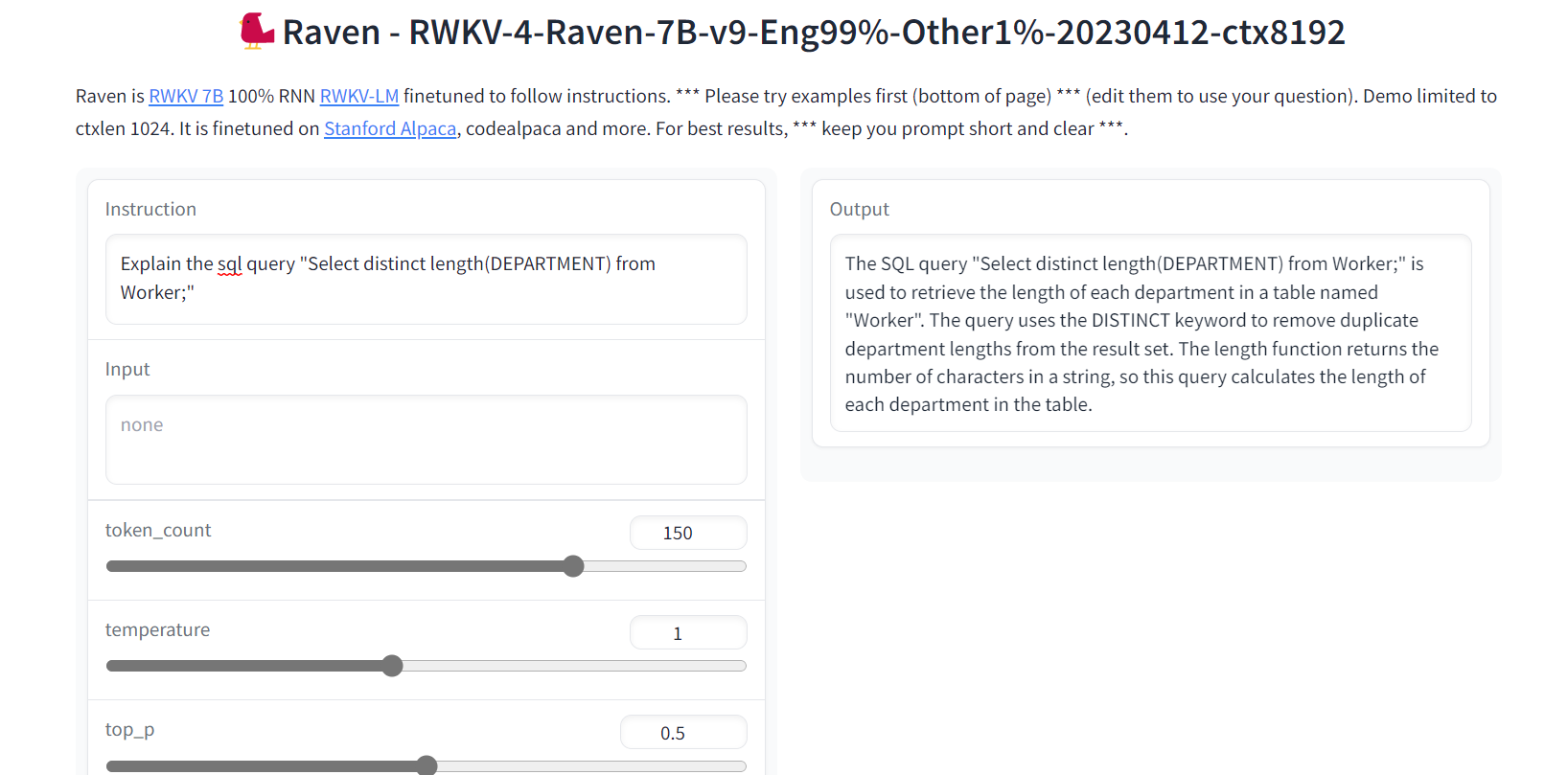
Image from Raven RWKV 7B
- GitHub: BlinkDL/ChatRWKV
- Demo: Raven RWKV 7B
- Model card: BlinkDL/rwkv-4-raven
6. OpenChatKit
OpenChatKit is a comprehensive toolkit that offers an open-source alternative to ChatGPT for developing the chatbot application.
The toolkit includes step-by-step instructions for training your own instruction-tuned large language model, fine-tuning the model, and an extensible retrieval system for updating the bot’s responses. Additionally, it includes both moderation features that can help filter out inappropriate questions.
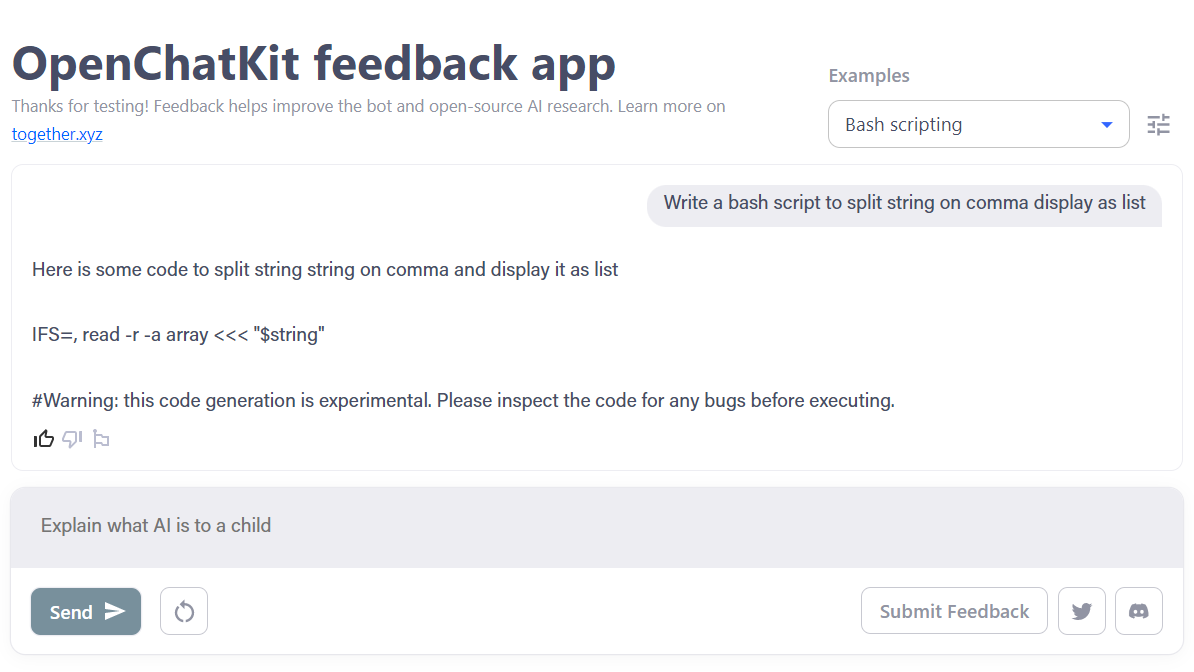
Image from OpenChatKit
- Blog Post: Announcing OpenChatKit — TOGETHER
- GitHub: togethercomputer/OpenChatKit
- Demo: OpenChatKit
- Model card: togethercomputer/GPT-NeoXT-Chat-Base-20B
7. OPT
OPT (Open Pre-trained Transformer) Language Models have demonstrated remarkable abilities in zero-shot and few-shot learning, as well as Stereotypical Bias analysis, despite not matching the quality of ChatGPT.
OPT is a family of large language models ranging from 125M to 175B parameters. The models are decoder-only transformers, which means they generate text autoregressive from left to right.
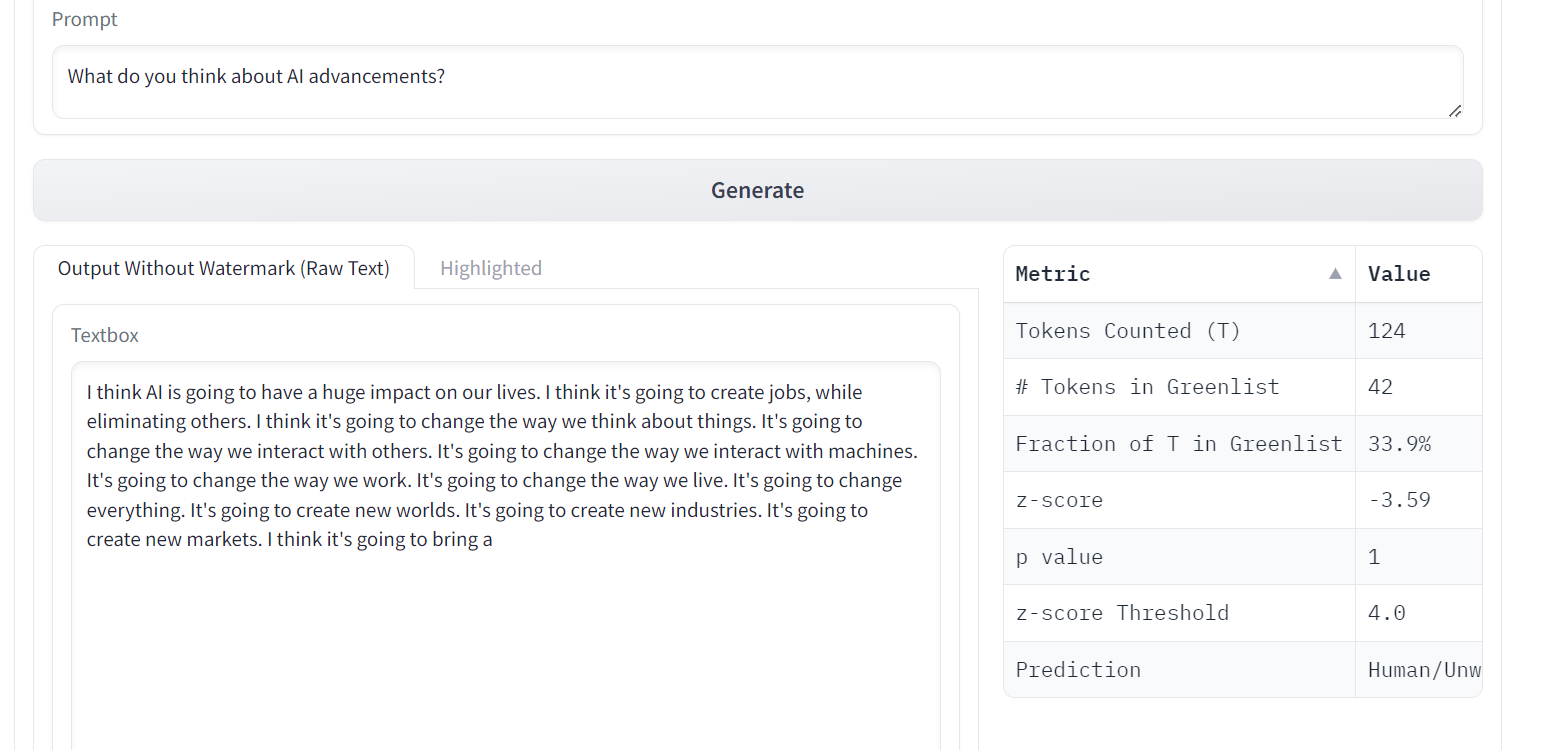
Image from A Watermark for LLMs
- Research Paper: OPT: Open Pre-trained Transformer Language Models
- GitHub: facebookresearch/metaseq
- Demo: A Watermark for LLMs
- Model card: facebook/opt-1.3b
8. Flan-T5-XXL
Flan-T5-XXL was fine-tuned T5 models that have been trained on a vast collection of datasets presented in the form of instructions. This type of fine-tuning has significantly improved performance on a variety of model classes, such as PaLM, T5, and U-PaLM. Moreover, the Flan-T5-XXL model was fine-tuned on more than 1000 additional tasks covering multiple languages.
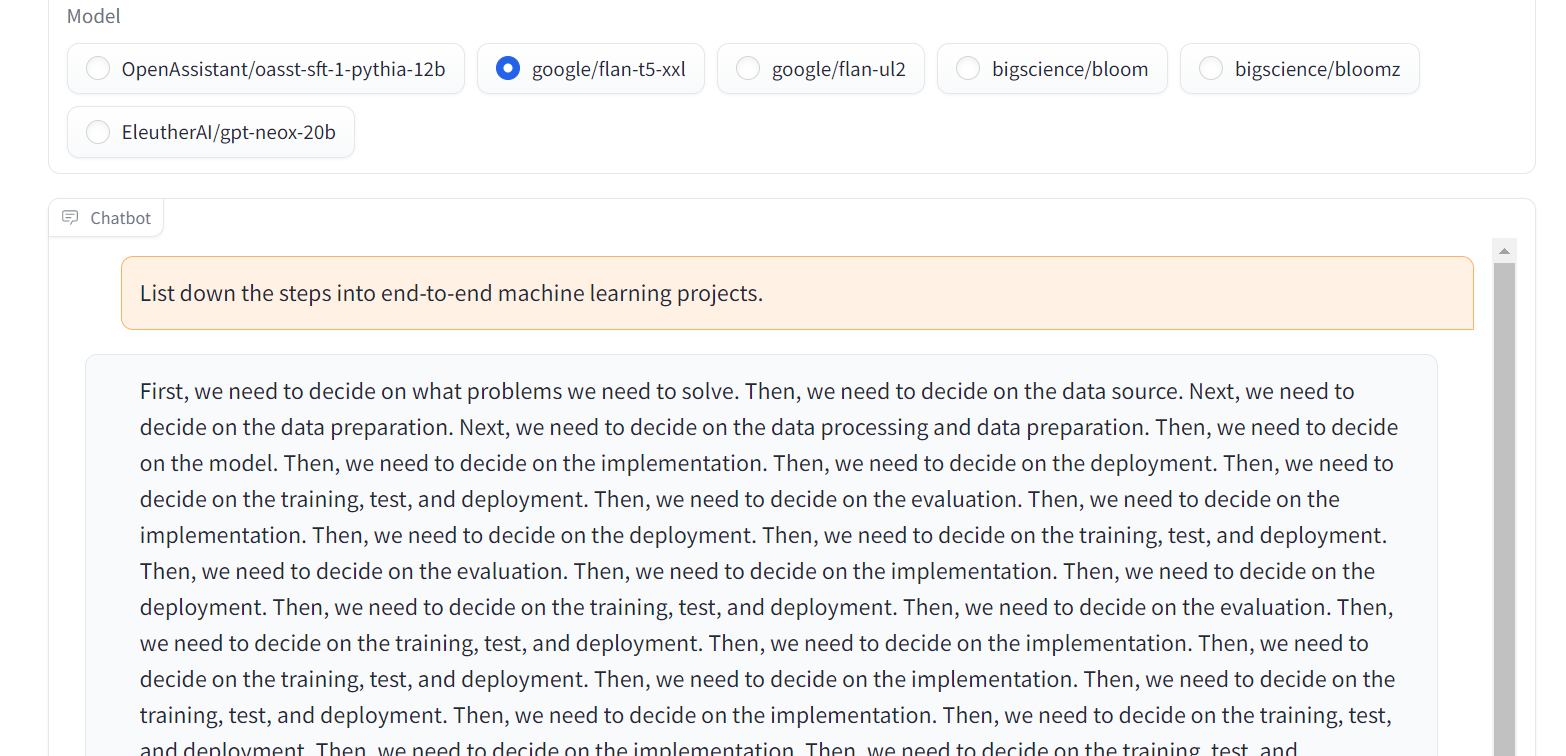
Image from Chat Llm Streaming
- Research Paper: Scaling Instruction-Fine Tuned Language Models
- GitHub: google-research/t5x
- Demo: Chat Llm Streaming
- Model card: google/flan-t5-xxl
9. Baize
Baize exhibits impressive performance in multi-turn dialogues thanks to its guardrails that help mitigate potential risks. It has achieved this through a high-quality multi-turn chat corpus, which was developed by leveraging ChatGPT to facilitate conversations with itself.
Baize code source, model, and dataset are released under a non-commercial (research purposes) license.
 Image from Baize 7B
Image from Baize 7B
- Research Paper: Baize: An Open-Source Chat Model with Parameter-Efficient Tuning on Self-Chat Data
- GitHub: project-baize/baize-chatbot
- Demo: Baize 7B
- Model card: project-baize/baize-lora-7B
10. Koala
The Koala is a chatbot trained by fine-tuning LLaMa on a dialogue dataset scraped from the web. Koala has performed better than Alpaca and is similar to ChatGPT in many cases.
Koala provides training code, public weights, and dialogue fine tuner, and it was evaluated by 100 humans.
Image from FastChat/Koala
- Blog Post: Koala: A Dialogue Model for Academic Research
- GitHub: young-geng/EasyLM
- Demo: FastChat/Koala
11. Dolly
Dolly is a large language model that was trained by Databricks machine to demonstrate that we can use old open-source language mode and give them ChatGPT magic instruction following ability. Model training requires 30 minutes on one machine, using high-quality training data. You don’t even require large models to achieve high quality. The team has used the 6 billion parameters model, compared to 175 billion for GPT-3.
Check out Dolly 2.0, an instruction-following language model that can be used commercially.
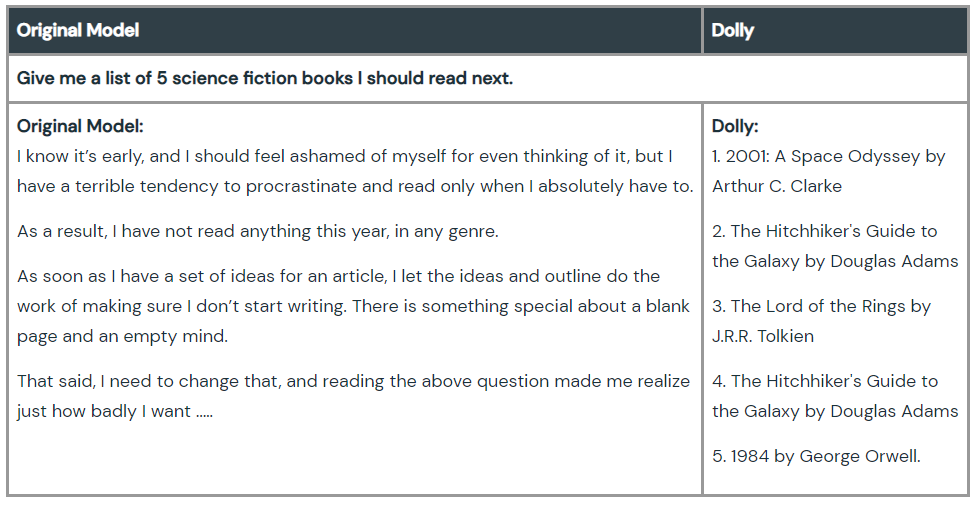
Image from Hello Dolly
- Blog Post: Hello Dolly: Democratizing the magic of ChatGPT with open models
- GitHub: databrickslabs/dolly
- Model card: databricks/dolly-v1-6b
12. Open Assistant
Open Assistant is a truly open-source project, which means giving everyone access to top chat-based large language models. It aims to create a revolution in innovation in language by enabling people to interact with third-party systems, retrieve information dynamically, and create new applications using language.
You can run the large language chatbot on a single high-end consumer GPU, and its code, models, and data are licensed under open-source licenses.
Image from open-assistant.io
- Blog Post: Open Assistant First Models are here!
- GitHub: LAION-AI/Open-Assistant
- Demo: open-assistant.io
- Model card: OpenAssistant/oasst-sft-1-pythia-12b
Conclusion
These GPT-4 alternatives can help researchers, developers, and small companies to create their language-based technology and compete with giants in the industry. The performance of the models is not above GPT-4, but with time and community contribution, some could have the potential to overtake GPT-4.
